April 2006
![]()
AutomatedBuildings.com
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
(Click Message to Learn More)
April 2006 |
[an error occurred while processing this directive] |
|
|
|
ABSTRACT
Heterogeneous photocatalysis, also referred to as photocatalytic
oxidation or PCO, is an emerging advanced oxidizing technology that offers many
opportunities for application in the HVAC industry. One of the most highly
anticipated uses is in providing energy-sensitive solutions to indoor air
quality challenges. A number of system design considerations should be given by
the specifying engineer toward maximizing the success of deploying PCO
technology in building HVAC designs. This article presents several of those
considerations to familiarize system designers with the process of applying PCO
technologies.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[an error occurred while processing this directive] |
INTRODUCTION
Photocatalytic Oxidation (PCO) is an emerging technology in the HVAC
industry that has great potential for application toward improvement of indoor
air quality (IAQ). In addition to the prospect of IAQ benefits, it has the added
potential for limiting the introduction of unconditioned air to the building
space, thereby presenting an opportunity to achieve energy savings over
classical prescriptive designs. As with other advanced oxidizing technologies,
sound engineering principles and practices should be employed by the building
HVAC designer to ensure proper application of the technology. The purpose of
this document is twofold: (1) to present a general overview of guidance
materials, standards and other considerations that should be taken into account
during evaluation of PCO for use in building HVAC designs; and (2) to introduce
a specific methodology for approaching the task of providing engineered designs
that successfully incorporate PCO and complementary technologies.
TERMINOLOGY
A short glossary of terms is included to familiarize the reader with the
similarities, differences and relationships between various technologies
addressed in this
document.
HETEROGENEOUS PHOTOCATALYSIS1
Photocatalysis taking place at the interfacial boundary between two phases
(solid-liquid; solid-gas; liquid-gas).
IAQ PROCEDURE2
ASHRAE 62.1 defines this as a design procedure in which outdoor air intake rates
and other system design parameters are based on an analysis of contaminant
sources, contaminant concentration targets, and perceived acceptability targets.
This procedure allows credit to be taken for controls that remove contaminants
(for example, air cleaning devices) or for other design techniques (for example,
selection of materials with lower source strengths) that can be reliably
demonstrated to result in indoor contaminant concentrations equal to or lower
than those achieved using the Ventilation Rate Procedure. The IAQ Procedure may
also be used where the design is intended to attain specific target contaminant
concentrations or levels of acceptability of perceived indoor air quality.
LEED CERTIFICATION3
The Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design Green Building Rating System
is a consensus-based national standard for developing high-performance,
sustainable buildings. Certification distinguishes building projects that have
demonstrated a commitment to sustainability by meeting the highest performance
standards.
PARTICULATE FILTRATION4
The capture of small airborne particles found in indoor and outdoor
environments. These particles include fibrous materials, solid-state
semi-volatile organic compounds, and biological materials.
PHOTOCATALYSIS5
The acceleration of a photoreaction in the presence of a catalyst. The
photocatalytic activity depends on the ability of the catalyst to create
electron-hole pairs, which generate free radicals able to undergo secondary
reactions such as oxidation.
PHOTOLYSIS5
A chemical reaction in which a compound is broken down by light. The direct
process is defined as the interaction of one photon with one target molecule.
ULTRAVIOLET GERMICIDAL IRRADIATION1 (UVGI
OR UVC)
Photolysis in which microbes are killed or neutralized by exposure to
ultraviolet light at wavelengths at or near 2537 Angstroms, or 253.7 nanometers.
Irradiation at this wavelength damages their molecular structure by altering DNA
and RNA.
VENTILATION RATE PROCEDURE2
ASHRAE 62.1 defines this as a prescriptive procedure in which outdoor air intake
rates are determined based on space type/application, occupancy level, and floor
area. Note: The Ventilation Rate Procedure minimum rates are based on
contaminant sources and source strengths that are typical for the listed space
types.
TECHNOLOGY INTERACTION
“The perception of indoor air quality is based on the interaction of a
complex set of variables including chemical, biological, physical and
psychosocial factors.
Concern about indoor air quality has been driven mainly by health problems
believed to be attributed to exposure to gaseous, particulate and microbial
contaminants.”6 Methods of addressing these types of contaminants
in building air streams have yielded successful results for improvement of IAQ.
As most occupied building spaces contain indoor air that harbor all three of
these contaminant types, a multi-layered approach to the use of common with
emerging technologies is often required to address the variety of contaminants.
Some of these technologies share complementary relationships with others and
lend themselves well to combined use.
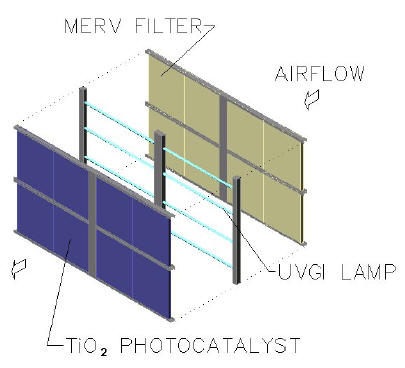
Figure 1: An exploded view of layered air treatment technologies adapted to the mixing box section of an air handling unit (Courtesy of Genesis Air, Inc.7)
An example of relationship complement between technologies can be found in the combined use of particulate filtration, photolysis and photocatalysis. With proper equipment placement and maintenance, particulate filtration can capture and remove from free circulation many dusts, pollens and other particulate matters in an air stream, while allowing smaller particulates, microbes and gases to pass through the filters. UVGI exposure can then neutralize many of the microbial contaminants that were not picked up by the particulate filters. With careful positioning and adequate density, photons emitted by the UV lamps can also activate the PCO process, allowing the creation of hydroxyl radicals that aggressively oxidize gaseous, particulate and microbial contaminants that pass through the media.
[an error occurred while processing this directive] Careful coordination of these technologies is paramount to their successful application in the improvement of indoor air quality. The efficiency of the particulate filter, described by its MERV4 rating, is affected by the velocity of the air moving across the filter. Refer to ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 52.2 for detailed information concerning MERV ratings and related performance parameters. Similarly, UVGI effectiveness is related to airborne contaminant velocity, since it is directly based on the intensity of photon exposure to the contaminant and to the amount of exposure time. As might be expected, PCO efficiency is affected by the velocity of air moving through the media, since it determines residence time, the amount of time the hydroxyl radicals have to complete the redox process. PCO efficiency is also dependent upon configuration to allow sufficient photon energy (3.2eV for TiO2) to reach the full surface of the semiconductor such that hydroxyl production can be maximized.
APPLICATION DESIGN OBJECTIVES
Indoor air treatment by layered PCO equipment is categorized in ANSI/ASHRAE
Standard 62.12 as an IAQ Procedure, which allows the design professional the
opportunity to choose an alternative to the prescriptive method, the Ventilation
Rate Procedure. The resulting benefits are designs that can minimize the
over-use of outside air to dilute odors and other contaminants, a procedure
often associated with high energy usage8,9, and in some instances, a source of
introduction of additional airborne contaminants to the building space.
The designer should conduct air stream sampling and constituent characterization to gain a clear understanding of which airborne contaminants are present prior to determining how to apply air treatment technologies to specific building spaces. If there are no opportunities for sampling and characterization, historical data relating to the quality of indoor air at nearby facilities of similar function and operating schedule should be examined. Data regarding outdoor air quality should also be gathered to account for the introduction of outside air to the building spaces of concern. Occupancy load data is necessary for the designer to gain a proper understanding of how airborne contaminants might be distributed within the building spaces. Process chemicals that are stored or applied within the building confines or adjacent exterior areas in communication with the target spaces must be documented and taken into account during design.
IAQ goals should be established for spaces under
consideration for air treatment, as well as means for determining adherence to
those goals. In areas such as
clean rooms, surgical suites, and other highly regulated spaces, IAQ criteria
are clearly defined. In spaces such as hotels, offices, classrooms, auto shops
and others, these criteria may not be as well defined. General use IAQ goals can
be adopted, but do not provide to the designer the level of guidance toward
proper application of treatment technologies that can be provided by specific
use goals. In addition to site-specific abatement needs, a number of
governmental, industrial, scientific and private concerns are currently
undertaking standards development efforts to set prescriptive categorical
threshold limit values for exposure to specific contaminants of concern. Design
professionals have the growing responsibility of keeping abreast of these
regulatory developments and implementing them in their facility designs as they
are adopted.
EQUIPMENT CONFIGURATION
Once contaminant species and concentrations are documented and IAQ goals are
established, the designer’s attention can turn to the task of matching layered
air treatment technologies to the building spaces in which they are to be
applied. Contaminant distribution profiles should be developed for each target
building space. Control volume models can be constructed to account for the
introduction and removal of air from zones. Contaminants introduced into the
zonal air streams by occupants and other generators can then be added to
complete the air distribution models.
Deployment of building air treatment technologies is accomplished by two methods, the first being system wide or general use, and the second being task-oriented or point-of-use. Often a combination of both methods is necessary for adequate treatment of the building air. Gaseous contaminants such as general odors and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can spread rapidly throughout a building and at times are not readily associated with a particular process or area, and so they are treated by incorporation of layered PCO equipment into the building HVAC systems. It is desirable, however, to treat contaminants that are segregated to identifiable spaces and comprised in part or wholly of visually detectable particulates or gases, with point-ofuse layered PCO equipment to prevent further dispersion of the contaminants throughout spaces that would otherwise not have co-mingled air streams.
Some geographic locales require building designs that treat outside air before it enters the building air distribution system due to high contaminant levels at the building exterior. Layered PCO can be used very effectively in this type of application.
While this discussion has focused primarily on fixed location PCO equipment usage, opportunities are also common for its use in applications that require portable equipment for abatement of contaminants, such as office space refurbishing operations, concert venues, conventions, and other short-term space-using functions.
In placing air treatment equipment on a project, the designer should always be cognizant of local building codes, ordinances and other applicable regulations, so as not to cause conflicts with life safety systems, fire and smoke barriers, space pressurization profiles, specialized air distribution systems, or other similar concerns.
ADDITIONAL CONSIDERATIONS
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
Advanced oxidizing technologies such as PCO systems readily support functional
enhancements commonly associated with building automation systems (BAS).
Standard practices of monitoring and reporting the loading of particulate
filters, amperage draw of UV lamps and operational status of fans are always
recommended. Additional monitoring of occupant load by indicators such as CO2 or
other methods, and of specific contaminants of concern, such as smoke obscurity
and VOCs, can increase the data available to the BAS for increased system
control. These monitoring points and control algorithms are supported by most
energy monitoring and control platforms, such as BACnet- or LonTalk- compliant
systems10,11.
Photocatalysis is considered to be a sustainable technology in that it functions to improve indoor air quality and minimize building energy usage, and does so without appreciable depletion of the semiconductor photo-catalyst. In certain designs, the opportunity may exist for LEED3 point standing to be increased due to the application of this technology to the building design.
As mentioned earlier, PCO can be applied in conjunction with other technologies to achieve specific design goals. In cases where granular activated carbon (GAC) systems are used to abate high concentrations of volatile organic compounds, PCO may be a good fit for placement upstream of the GAC unit to reduce contaminant concentration prior to entering the GAC filters, thus prolonging the useful life of the GAC media and reducing the cost of recharge or replacement. In similar fashion, layered PCO technologies could be positioned adjacent to energy wheels or air handling unit coils such that the UVGI lights could bathe the equipment to preclude the promotion of unwanted microbial activity.
IN SUMMARY
A layered approach to the design and application of photocatalytic,
photolytic and other advanced air treatment technologies allows for
complementary technologies to work together to improve the overall efficiency of
the contaminant abatement effort. A clear understanding of contaminant types,
sources and levels should be gained in order to effectively design and apply the
treatment equipment in buildings or other enclosed spaces. Consideration should
be given to ventilation requirements for occupant load, space pressurization and
building equipment needs. Facility air distribution patterns should be studied
and fully understood such that placement of air treatment equipment will not
disrupt the proper function of other building systems. Methods should be
established to monitor performance of IAQ improving technologies, and
preventative maintenance schedules should be employed for the equipment.
Placement of PCO units should be made to address system-wide and/or point-of-use
solutions to specific contaminant problems. With proper consideration to these
design criteria, advanced oxidizing technologies can have dramatic impacts on
the improvement of indoor environments.
REFERENCES
V. Parmon, A.V. Emeline, N. Serpone. International Journal of Photoenergy, 2002. IUPAC Project #2002-036-1 “Glossary of Terms in Photocatalysis and Radiocatalysis.”
ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 62.1- 2004 “Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality.”
U.S. Green Building Council LEED Standard “Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design.”
ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 52.2-1999 “Method of Testing General Ventilation Air-Cleaning Devices for Removal Efficiency by Particle Size.”
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki, 2005. Internet-Based On-Line Encyclopedia.
L. Stevens, J.A. Lanning, L.J. Anderson, W.A. Jacoby, N. Chornet. AWMA 1998. 98-MP9B.06 “Photocatalytic Oxidation of Organic Pollutants Associated With Indoor Air Quality.”
http://www.genesisair.com, 2005. GAP™ Layered Photocatalytic Oxidation Technologies by Genesis Air, Inc.
ANSI/ASHRAE/IESNA Standard 90.1-2004 “Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residential Buildings.”
D.J. Branson, 2004. Engineered Systems Magazine December 2004 “Photocatalysis: Raising the Stakes for IAQ.”
ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 135-2004 “BACnet – A Data Communication Protocol for Building Automation and Control Networks.”
ANSI/EIA/CEA-709.1-B-2000 LonTalk Standard “Control Network Protocol Specification.”
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
David J. Branson, P.E. is a consulting engineer and Co-Founder of Compliance
Services Group, Inc., Engineers, Architects and Scientists in Lubbock, Texas,
where he currently serves as Executive Vice President. He is active in ASHRAE as
a participant on several Society and Technical Committees, with special focuses
on indoor air quality and building automation. Mr. Branson has designed and
deployed PCO technologies in numerous applications, including casinos, pathology
labs, hobby shops, classrooms and facilities for the U.S. Departments of Defense
and Homeland Security. Mr. Branson may be contacted by email at
djbranson@csg.net.
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
[Click Banner To Learn More]
[Home Page] [The Automator] [About] [Subscribe ] [Contact Us]