July 2010
![]()
AutomatedBuildings.com
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
(Click Message to Learn More)
July 2010 |
[an error occurred while processing this directive] |
|
|

Nirosha Munasinghe MBusIT BSc BE (Hons) (Melb) |
The infrastructure underlying the Building Automation Systems has evolved with technology over the last decade. The software applications managing the BAS has progressed from a simple dedicated PC to dedicated file and web servers. Today the concept of a virtual server is real and is used in a variety of industries to optimize their business processes and operating costs. As the BAS industry transforms to web based systems and into cloud computing models, virtual servers are a reality for BAS. This article examines what a virtual server is and the implications it has on the BAS market.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[an error occurred while processing this directive] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[an error occurred while processing this directive] |
A virtual server is a software implementation of a physical computer that executes application programs. Therefore each physical server can have multiple virtual servers each with its own operating system executing its own application.
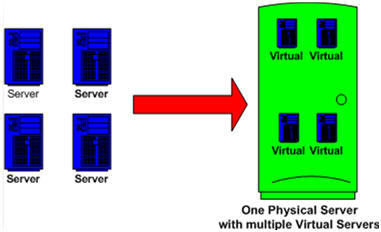
Figure 1: Multiple physical servers can be moved into one physical server
having multiple virtual servers performing the same functionality.
As shown in figure 1, each of the virtual servers running on the physical server operates independently of each other sharing the physical resources such as memory and disk space of the physical server. What is the benefit of such a setup to the BAS market?
Increase Efficiency of IT
infrastructure
A typical building’s control room consists of software to monitor air
conditioning controls system, security system, asset management system and
database for collecting data for energy reporting. In most instances, these
applications are executed in separate PC/Servers to avoid conflicts in shared
resources of the operating system executing the application. For example each of
the applications could require SQL SERVER, certain windows services and
registries; therefore most software vendors recommend executing the applications
on separate servers to avoid conflicts and to simplify support management. The
implications of such setups are:
Very low utilization of each of the servers. Although the server may spike up to its maximum at certain times, on average it may be using around 20% of its capacity.
Most of the data storage capacity in the server is not used by the application. Therefore large amount of data is under utilized.
A large capital is required to purchase individual servers/PC for each application.
As the server count grows, the network grows, implying a requirement for more support staff to maintain the infrastructure. A large percentage of the IT budget must be allocated to the maintenance and on going support of the system.
In a virtual server environment each of the applications can run on its own operating system on a single physical server without competing for resources or conflicts. As shown in figure 2 the air conditioning controls, security, asset management, and energy management systems operate on individual virtual servers without conflicting processes.
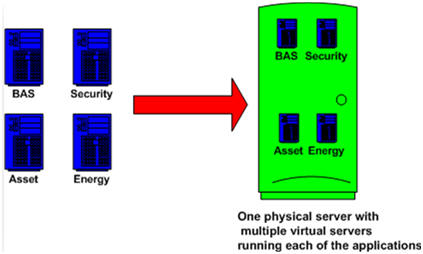
Figure 2: Various applications of building management running on virtual servers.
For the application vendor support staff, it is the same as running the application on independent physical servers, therefore the process of support management for the vendor is transparent. One of the biggest advantages of the virtual server is the cost reduction in hardware, and IT support on managing issues with the physical server. The cost reduction is from savings in depreciation of the hardware, rack servers, OS upgrades, IT supports salaries and outsourcing agreements. This improves the productivity of the IT staff enabling them to concentrate on being responsive to improving the business needs.
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
Energy Savings
Today, a key challenge to a facility management department is to reduce
consumption of energy to lower the carbon footprint. Using virtual servers is
another tool that can assist the challenge of energy management. It can be
argued that the consumption of electricity by one or two physical servers in a
small building can be insignificant. However, as the cost of electricity rises
around the world, the annual cost of powering a server will soon exceed its
acquisition costs. Therefore the electricity consumption of running servers will
be significant to both small and large multi national sites. It’s not only the
direct electricity required to operate the servers, but the large amount of energy
required to cool the servers and the large real estate space of the control
room. For example; a multi national hotel having a dedicated server for the BAS at
each location could be small for each hotel but the accumulative electricity
costs in running the servers is significant. Also, as most servers
are under utilized, the electricity consumed by the server is a wastage of energy.
Virtual servers are more dynamic and responsive to fluctuating capacity
requirements and have dynamic resource schedulers to regularly balance the
resource pool on the physical server. They also contain dynamic power management
to reduce power consumption by turning off servers when there is unneeded
capacity without affecting applications or end users. The bottom line is that
studies have proven that using a virtualized server saves 7000 kWh of electricity
and four tons of carbon dioxide per year.
Easier and Faster Deployment
Virtual servers can assist BAS vendors and system integrators deploy
the BAS applications by a much faster and easier process than deploying each
project on a single
physical server. To examine the powerful deploying features in
a virtual environment, let’s examine an example of a multi national hotel
installing a BAS at each of their world wide locations. The general steps taken
to deploy the BAS application on a single physical server for each location as
follows:
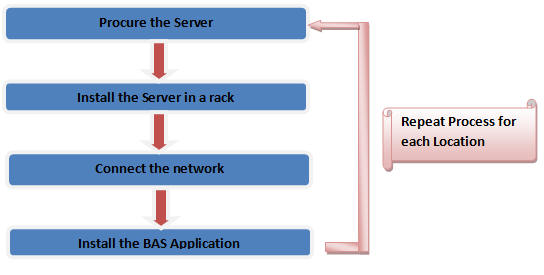
Figure 3: Process of installing BAS application on single physical servers.
The process of server procurement, installation of the server in rack and connecting to the network requires multiple technicians and network administrators, generally requiring weeks to complete. The process of installing the BAS application involves installing and configuring databases, windows services etc… requiring reading of manuals and multiple support calls to the BAS vendor. The most redundant part of the process is then repeating each of the steps for each job location, increasing costs without any productive work.
In a virtual server environment the BAS application vendor or the system integrator has the ability to install the BAS application into the virtual server. This involves installation of the actual application and any associated services to the application such as databases, window services and debugging tools. Once the entire application is installed in one virtual server, it has the ability to copy the entire virtual server into a physical medium for other deployments.
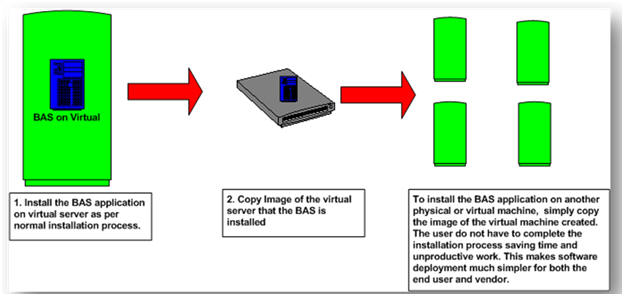
Figure 4: Benefit of application deployment in a Virtual Environment
To install the BAS application on another physical server, or on anther virtual server setup on the same physical server, only requires copying the BAS application already installed. There is no requirement to install or configure the system. Therefore multi-deployment in a virtual server environment can be achieved rapidly, reducing redundant and unproductive costs.
It is clear that virtual servers reduce the operating costs of the facility department, reduce energy consumption and streamline the IT support management process. There are many virtual server vendors’ offering various flavours of virtual machines and the technology has matured over the last decade for the BAS vendors confidently utilizing it to their advantage. Now it is up to us to promote the technology to the end users to rollout the technology into the BAS market.
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
[Click Banner To Learn More]
[Home Page] [The Automator] [About] [Subscribe ] [Contact Us]