June 2009
![]()
AutomatedBuildings.com
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
(Click Message to Learn More)
June 2009 |
[an error occurred while processing this directive] |
|
|
|
Whether social or physical our evolving Building Automation Networks require our closest attention and need to be carefully nurtured to grow strong while incorporating every sustainable future possibility. This article provides insight to the evolution to date of Building Automation Networks to Enterprise and Web based networks and on into cloud computing.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[an error occurred while processing this directive] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[an error occurred while processing this directive] |
Pushing the
Envelope - comment by Andy McMillan, President, BACnet International
Celebrating past effort and current success is necessary but not sufficient in
our rapidly changing world. We also need to accelerate development in the BACnet
community to address new requirements and accommodate new technologies. It was
clear at the last conference that in several areas products and applications are
pushing the envelope of the current specification. Web service applications,
wireless devices and multi-device object models are a couple of areas where
application requirements are driving suppliers to go beyond the limits of the
current standard.
Unified System Architecture
LonMark International
The future of building systems seems clear. IP has become a key, pervasive
element of networking technology at the enterprise/IT level, and LONWORKS®
technology and products at the field level. Enterprise Connectivity, the method
for connecting the building control network into the data network – known as the
LON-LAN-WAN architecture. This ensures that the control system becomes an
element of all the data sources available to the enterprise. Open interfaces
have been developed to ensure data communication between the LON (the building
control network) and LAN (Local Area Network) is accessible by a vendor. To
provide this connectivity, enterprise level infrastructure devices are needed,
and they must be specified as open. Standard routers are used which means no
gateways are required.
New generation of integrated security
solutions, based upon the NiagaraAX Framework® from Tridium
Many advances have been made in the development and deployment of video-based
security systems. Yet many of these video devices remain isolated from other
critical building systems and are therefore limited in their usefulness and
coverage. Standalone video monitoring/alarming systems, while important, are
just the first steps towards achieving a complete security solution. To optimize
the true value of your video systems, you need to integrate these video devices
with existing energy, HVAC, building automation, and security management systems
to create a new level of visibility into – and resolution of – facility events
as they occur.
Executives today face three key challenges as they look to maximize the
performance of their facilities and the safety of the work environment:
1. How do you turn today’s traditional isolated security silos into integrated
components of a larger building-wide solution and transform conventional
facilities into dynamic, flexible Intelligent Buildings?
2. How can you optimize, extend, and protect your current investment in video
equipment?
3. And how can you do it quickly and cost-effectively?
Video the Newest BA Network
From an interview with Marc Petock, Vice President, Global Marketing &
Communications Tridium and myself
Sinclair: What is Niagara Video?
Petock: Niagara Video is our latest application in providing a comprehensive intelligent building solution that integrates all the common building functions-environmental control, intrusion detection, access control, lighting and energy management with video. It provides seamless integration between today’s building applications and digital video recorders, IP cameras, network video recorders, and video management solutions.Sinclair: Can you give me an example?
Petock: Let’s use the following scenario: It is Saturday
2:05 a.m. - A facilities BAS system reports a low temperature alarm from the HVAC system.
2:05 a.m. - Simultaneously, as this alarm is being generated and notification is being sent to authorized personnel, the security system automatically re-directs a camera to view down the hallway in the direction of the alarm.
2:07 a.m. - Personnel look at live video; turn hallway lights on; see water leaking from the ceiling; shut down HVAC system and calls for emergency repair-all remotely and in real time.
2:08 a.m. - Immediate action is taken, a disaster is averted, overall damage and repair costs held to a minimum and overall risk is mitigated.Sinclair: What led Tridium to develop this application?
Petock: Today’s building owners and facility managers are faced with several challenges as they look to maximize the performance of their facilities and look to extend the investment in their video management systems. While many advances have been made in the development and deployment of video-based monitoring systems many of these remain isolated from other critical building systems and therefore are limited to their usefulness and coverage. To optimize the true value of video systems they need to integrate directly with existing systems such as HVAC, energy management, lighting and security to create a new level of real-time visibility into-and resolution of facility events as they occur. We believe that turning traditional isolated building video and security silos into part of an integrated, building-wide facility management solution would further optimize these systems. And with Niagara Video it does.
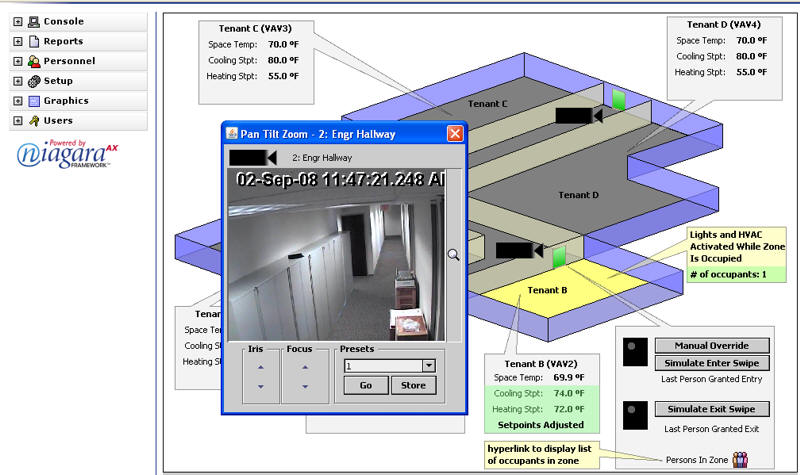
Sinclair: Is it built using the Niagara Framework?
Petock: Yes, so it can merge with other security and video products to provide a complete building automation, card access and video monitoring system or it can be used as a stand alone system providing a video window that identifies an incident and notifies the proper personnel who can manage the response from anywhere. Niagara Video can be combined with other NiagaraAX applications to deliver a unified, intelligent facility-wide management system that is easy to use, easy to understand and easy to commission.Sinclair: You mentioned that Niagara Video contains bi-directional alarming. What do you mean?
Petock: The alarming component of Niagara Video is bi-directional so it can initiate video recording of critical events based on Niagara alarms as well as control building functions and view live video in Niagara based on video system events. For example, a flame event in a boiler room can automatically re-direct cameras and record the event, storing the critical video clip in a protected video alarm database for future reference. Conversely, an alarm from a video device, such as a video motion detection alarm, can initiate control logic sequences-such turn on the hallway lights or building lockdown-when a camera sees unauthorized motion activity.Sinclair: Does it work in local and remote buildings?
Petock: Niagara Video works with local and remote buildings equally as well. The flexibility and scalability of the solution also provides users with visibility into an entire facility or group of facilities via a single browser-based user interface. This allows system users to manage facility events and information from any location without requiring dedicated computers or thick client software.Sinclair: When will this be available?
Petock: Niagara Video will be available for general release on February 15, 2009.
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
Why Internet Protocol?
- George Thomas, President, Contemporary Controls
Connecting BACnet Devices to an IP Infrastructure This
paper reveals how all BACnet devices can effectively share a common IP network —
thereby enhancing the power and convenience of BACnet.
IP is important for reasons other than convenience. Building automation systems
and information technology (IT) are quickly converging with both areas sharing a
common IP network. This IP network is the quickest way to gain access to the
Internet which is the world’s wide-area-network (WAN). All modern communication
networks are IP-based even if communication is restricted to local-area-networks
(LANs). Modern buildings are designed and built with structured wiring in mind
with integrated telephone and data wiring that can operate at Gigabit Ethernet
speeds. Why run proprietary fieldbus networks when structured cabling is already
in place? Even non-BACnet building automation systems are connecting to IP —
including access control systems, security systems, life-safety systems, and
lighting systems. LON-based systems are using the IP networks as a tunnel taking
advantage of “free” wiring.
When we think of IP networks we think of Ethernet with speeds of 10, 100 or 1000
Mbps running over CAT 5, CAT 5e or CAT 6 twisted-pair cabling. These same speeds
can be achieved over multimode or single-mode fiber optic cabling as well.
Granted, the higher speed connections are wired, but there are plenty of
wireless technologies that attach to IP networks. It is clear that the backbone
of choice is IP.
ZigBee a wireless standard
ZigBee platform is widely used to create reliable, self-healing and scalable
wireless networks that enable solutions in building automation, energy
efficiency, HVAC, AMR, predictive maintenance, asset tracking, and other
application areas.
The ZigBee Alliance is an association of companies working together to enable
reliable, cost effective, low-power, wirelessly networked monitoring and control
products based on an open global standard. The ZigBee Alliance membership
comprises technology providers and original equipment manufacturers worldwide.
Membership is open to all. Additional information can be found at
www.zigbee.org.
Connecting networks to unconnected legacy
devices
Facility managers can now use new technology like the Wireless Steam Trap
Monitor (WSTM) from Cypress Envirosystems to detect steam trap failures almost
immediately, and to repair or replace the defective units. This technology
non-invasively clamps on top of steam traps, performs monitoring and diagnostics
and transmits health status wirelessly to a central receiver and server for
monitoring, trending, graphing, alarming and historization. Each WSTM installs
in minutes, and does not involve breaking seals, leak checks, or system
downtime. The WSTM data can be shared with existing building automation systems
via BACnet/IP or LON, so no new software or operator training is needed to
implement this solution
Wireless Gauge Reader (WGR) is essentially an “electronic eyeball” which can be
clamped onto the front of a gauge in minutes, without removing the existing
gauge. It optically reads the needle, converts to a digital reading, and
transmits it wirelessly to a central receiver/server. The data can then be
accessed virtually anywhere via a web browser or PDA, or be transferred to an
existing BAS via BACnet/IP, LON over IP or OPC.
A new patent pending product from Cypress Envirosystems, the Wireless Pneumatic
Thermostat (WPT), accomplishes the same retrofit in less than 20 minutes, for
less than 20% of the cost of conventional DDC. This means that retrofits can be
performed right away, even while a building is fully occupied, and achieve
payback periods of about one year.
Enable OPC UA to integrated existing building
systems architectures
OPC Unified Architecture (OPC UA) is designed to maximize the power of XML to
provide robust communication, and secure data exchange, through a services model
in an extremely scalable way.
OPC and OPC UA are the answer to the problem of securely transferring data
between independent systems, or systems with non compatible protocols. Data can
be provided to decision makers at all levels so that they can make effective
decisions, and continue to focus on growing their business in the current
economic environment instead of worrying about their data flow.
Check out the OPC Foundation website at
www.opcfoundation.org
Distributed approach for Enterprise
Building Management Systems
Toby Considine, Technology Officer, Facility Services,
University of North Carolina – Chapel Hill states in his column
Cyber-security, Smart Buildings, and the Smart Grid
We went to a distributed approach for EBMS, something that looks nothing like
the approaches of traditional building systems and of SCADA. I can now upgrade
parts of the infrastructure by replacing a single autonomous system agent in a
single location. The deep intimacy that old integrations required is gone, and
the reliability and resilience of the system is improved. This means it is
possible for me to roll out incremental security fixes, or even system agents
from a different platform, without spending years and re-training all.
How do accessible networks at all levels
provide value?
OpenEMS a column by Andy McMillan, President and CEO
Teletrol Systems Inc.
http://www.automatedbuildings.com/news/apr09/columns/090330025517mcmillan.htm
Talks about “Creating Value Through Open Systems In An Energy Management
Context”
OpenEMS (Open Energy Management Systems) is a philosophy of doing
business where energy-related product and service providers collaborate and
interact through standards-based solutions to deliver maximum value to building
owners and operators. In an OpenEMS environment, while equipment, software and
services may come from different providers they interoperate quietly and
efficiently in the background -- allowing building owner/operators to focus on
their core business.
There is typically a broad range of suppliers making up the “energy ecosystem”
for an owner/operator. The owner/operator may work with utilities, mechanical
service providers, alarm monitoring services, bill-pay-audit services,
electrical contractors, sustainability consultants, demand-response aggregators
and other energy-related product and service providers. Whether these providers
are external suppliers or internal service groups, they are all part of the
process of acquiring, using, controlling and managing the use of energy in a
building.
One way to view an energy ecosystem is to think of it as a building
owner/operators supply chain for energy. It includes all of the organizations
that impact the sourcing, utilization and management of energy. Just like in
manufacturing and retail supply chains, there are substantial value creation
opportunities in improving the efficiency of interaction among the stakeholders
in an energy ecosystem. OpenEMS is about accelerating the flow of information
among those stakeholders while reducing the cost of transactions … and these can
dramatically increase efficiency.
Improving the efficiency of interactions through links among business processes
and information systems serving stakeholders in an energy ecosystem yields
maximum owner/operator value. OpenEMS is the most cost-effective way to link
these systems and share required business and technical information among the
broad range players. This will result in substantial gains that flow to all of
the stakeholders and benefit everyone through lower overall costs of doing
business.
The animations from the web site provide a clear picture of all the advantages.
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
Clouding your networks;
extracted from another column by Toby
http://www.automatedbuildings.com/news/aug08/columns/080730055505considine.htm
Cloud Computing is a name for putting computing services, such as web services and Software as a Service, (SaaS), on computers up in the wider network.
Traditional control systems have no clouds – only towers in the sky. Whether or not it makes sense, building systems from one building or many have traditionally gone up to a central point; they have been a silo reaching up into the clouds.
For Brandl, nearly everything is a cloud; only the core control processes are on the ground. I think this is right; for buildings, only the core processes, those elements on the traditional low voltage protocols such as BACnet and LON, are on the ground.
Enterprise energy monitoring and building control, then, are in the low lying cumulus clouds. A well architected system does not put the EMCS center in the center of any control loops. TCP/IP is by design a non-deterministic protocol, meaning it does not belong inside a control loop. Anything off the ground is in the clouds. Anything in the clouds should interact using internet protocols.
In the UNC Enterprise Building Management (EBMS) project, we restrict all low level controls to the building. All communications outside the building are using internet protocols. Each building has its Enterprise Building Local Gateway (EBLG) speaking traditional standards and proprietary protocols on the building side, and web services on the outside. We keep the EBMS close to the buildings as a business decision, but there is nothing on the architecture that would prevent us from moving this service up into the higher up stratus cloud layer, or even up into the high flying cirrus layer.
The middle tier of stratus clouds is outside Facilities Operations and hosted in the wider enterprise. We plan for the Registrar’s Office, in the stratus cloud, to submit room schedules and head counts for every classroom down to the buildings. For now, this communication will have to be with the cumulus layer, but we would like to push it down to the ground at the building gateway.
We have long used building analytics products like Packrat at UNC, bolted onto the silo. It would be far better for these services to live in the cirrus clouds, under the direct control of someone with the in-house expertise to process the data into information. The processing necessary to turn operating data into predictive maintenance work orders is intense, but only needed sporadically. The whole purpose of cloud computing is to reduce costs by sharing expertise and resources so they are fully utilized. Building analytics should move up into the highest clouds, with the highest expertise.
The remotest services all belong in the Cirrus clouds. Demand/Response, Energy Markets, third party maintenance, all are Cirrus tier cloud services.
Keep some clouds close to you, ones in which fast response and control are the most important. Let some clouds drift up into the atmosphere, where forces out of your control may determine their performance and availability, but where superior resources or specialize knowledge can be purchased. And put services where enterprise identity and line of business interaction are the most important in the stratus layer.
Just remember, changing business conditions can move any cloud up or down. The protocol for communication to any cloud layer should be the same; internet ready, secured, and standards based, ready for e-commerce. Nothing but web services belongs anywhere in the clouds.
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
[Click Banner To Learn More]
[Home Page] [The Automator] [About] [Subscribe ] [Contact Us]