|
October 2020
AutomatedBuildings.com
|
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
(Click
Message to Learn More)
|
The Future of Access Control in Automated Buildings
The coronavirus pandemic has disrupted the world and
made safety more important than ever. Employers are now responsible to
provide healthy and safe workplaces and many are looking to access
control solutions to do just that.
|
 Staff Writer at Swiftlane, Staff Writer at Swiftlane,
Imran Anwar has 10+ years of professional writing experience about
technology-related topics including digital marketing, cloud computing,
SaaS, mobile apps, artificial intelligence, IoT, face recognition, and
building access control systems
|
The coronavirus
pandemic has disrupted the world and made safety more important than ever.
Employers are now responsible to provide healthy and safe workplaces and many
are looking to access control solutions to do just that. A recent Markets and Markets report predicts the highest growth rate for biometric reader-based access
control systems. What is biometric access control and is it the best type of
access control for the post-COVID-19 workplaces? Let’s take a look.
Biometrics: The Natural Born Credential
According to Science Direct, a simple definition of biometric technologies is as follows:
Biometric technologies generally refers to
the use of technology to identify a person based on some aspect of their
biology.
The Biometrics Institute, which represents a
multi-stakeholder global community, defines at least 15 types of biometrics, including DNA, fingerprints, facial, iris, retina, gait, odor,
voice, and others. But not all of them are used for access control.
Biometrics and Access Control
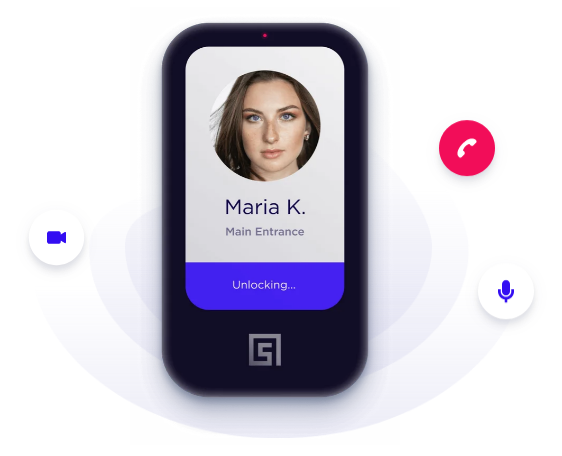 Biometric access control involves the use of the
individual’s
biological data to allow or deny access to a facility or certain areas of a
facility. The types of biometrics most commonly used for access control
include:
Biometric access control involves the use of the
individual’s
biological data to allow or deny access to a facility or certain areas of a
facility. The types of biometrics most commonly used for access control
include:
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology makes use of
artificial intelligence and computer vision to read and recognize faces. The facial recognition access control
systems include a face reader
that captures the face of the subject, converts it into a digital signal, and
sends it to a cloud-based or on-site server for matching with authorized face
credentials. Access is granted if the presented credential matches the stored
credential and denied if there is no match.
Iris or Retina Scanning
A retinal scan identifies the most unique
pattern of blood vessels in a person’s retina. It is performed by casting an invisible beam
of low energy infrared into the person’s eye when they look
at the scanner. The major limitation of retinal scanning is that the person has
to focus on the scanner’s eyepiece from about three inches away. This biometric
technology is rarely used for building or office entry, but is often deployed
at high-security facilities that only a handful of people are authorized to
access.
Fingerprint Scanning
Fingerprint scanning provides an inexpensive and
quick way to control access at offices. Fingerprints cannot be duplicated and
are a reliable biometric credential that can be tied to a specific individual.
They have been used in forensics as well as access control and attendance
management since the 1970s. But the outbreak of COVID-19 has made contact-based
scanners unsafe for access control. As a result, the sales of contact-based
fingerprint scanners are forecast to decline by $1.2 billion this year.
Where Is
Biometrics Access Control Best Deployed?

Biometrics is the only form of credential that
can be permanently tied to an individual, which makes it very effective for law
enforcement, subject tracking and forensic investigations. Biometric access
control is most often used at workplaces where a high level of security is
required. That seems like every other workplace these days.
Iris and retina scanning are deployed at
immigration and border control, secret government facilities, research
laboratories such as CERN, and other facilities that require an exceptionally
high level of security.
Facial recognition technology was widely
deployed for security and clandestine subject identification at airports and
border controls after 9/11. Today, many private businesses including Amazon,
MasterCard, Chevron, Tesco, Walmart, McDonald’s and many other companies are using or planning to use facial recognition for a variety of
purposes—from authenticating payments to analyzing moods.
Fingerprint scanning is used at banks for
account holder verification and at all types of offices for physical access
control and time and attendance management. Touch-based fingerprint scanners
are likely to take a hit because of COVID-19 and may lose market share to
touchless access control systems.
Benefits of Biometrics
Employee Management: Biometrics is a
reliable way of knowing who went in through the entry and exit and for how long
they were in the office. It helps improve employee accountability, particularly
if you have a workplace where people work in shifts at night and on weekends and
holidays.
Quick Enrolment: You don’t
have to print key cards or badges. A fingerprint scan or face photo is all you need to enroll people
into the system. With Swiftlane face recognition access control, for example,
the user just has to snap a photo of their face to get enrolled.
Fast Check In: With face recognition access control, users don’t need to pull out keycards or mobile phones from their
purse or pocket and can unlock the door by looking at the face reader. It’s
a major advantage at busy entries and can prevent queues from forming as people
line up for scanning their badges.
Enhanced Efficiency: With biometrics, you
don’t
have to worry about lost, forgotten, or stolen badges. It saves tons of time
and allows security teams to focus on other things rather than printing and
issuing badges on a daily basis.
Extra Security: Biometric credentials are
more secure than mobile credentials or key cards. Keycards, fobs, and badges
can be lost, stolen, or duplicated, apart from having many other limitations.
The use of biometrics also makes it possible to implement dual authentication,
which is the holy grail of security these days.
Low Maintenance Cost: Once the biometrics
access control is installed, there’s almost no maintenance cost to be paid. You don’t
have to invest in a printer or waste money on printing and mailing cards,
badges or fobs.
User Convenience: Mobile, PIN and card
based access control systems create friction when someone forgets their card,
forgets the PIN or has a dead phone battery. With biometrics, there’s
no chance of forgetting or missing anything.
Health and Safety: The COVID related
guidelines require the minimization and continual cleaning and disinfection of
common-touch surfaces such as keypads and touch screen displays. Contact-based
fingerprint scanners also fall under the category of common touch surfaces, by
face recognition biometrics coupled with automatic doors allow people to unlock
the door and enter the premises in a completely touchless way.
Scalability: Biometrics access control is
suitable for a small local business as well as global enterprises. Contemporary
biometrics systems have a lot of flexibility and can easily accommodate
additional employee data. Cloud-based biometrics systems can be easily scaled
to manage multiple locations via a single dashboard that can be used from
around the world.
Integration: Being cloud-based, modern
biometrics systems can be integrated with other building security and
management systems such as security alarms, video intercom, surveillance
cameras, HVAC, and visitor management systems.
Fast-Forward to the Future
Just as the pandemic continues to underline the
importance of creating safer workplaces. biometrics is forecast to be the fastest growing access control
technology between 2020 and
2025. Facial recognition access control, with a projected growth rate of 16.6%, is likely to overtake other types of biometrics. Would you say
using facial recognition for access control at commercial buildings is a good
idea? Let us know in your comments!
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
footer
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
[Click Banner To Learn More]
[Home Page] [The
Automator] [About] [Subscribe
] [Contact
Us]