It’s time for Carrier Grade Wireless Communication for BAS Industry

MBusIT BSc BE (Hons) (Melb)
|
March 2012 |
[an error occurred while processing this directive] |
|
Bluetooth, Zigbee, WiMax: What is it?
It’s time for Carrier Grade Wireless Communication for BAS Industry |
 Nirosha Munasinghe
MBusIT BSc BE (Hons) (Melb) |
| Articles |
| Interviews |
| Releases |
| New Products |
| Reviews |
| [an error occurred while processing this directive] |
| Editorial |
| Events |
| Sponsors |
| Site Search |
| Newsletters |
| [an error occurred while processing this directive] |
| Archives |
| Past Issues |
| Home |
| Editors |
| eDucation |
| [an error occurred while processing this directive] |
| Training |
| Links |
| Software |
| Subscribe |
| [an error occurred while processing this directive] |
Wi-Fi, ZigBee, Bluetooth, WiMax; what does this all mean? As the BAS
industry continues to integrate and articulates interoperable
solutions, the wireless communication medium is becoming an economical
solution for both new and retrofit buildings. A plethora of communication
standards are available from low distance, low powered to
high carrier grade protocols. Which standard fits the building
automation applications? ALL. As the industry diversifies to integrate
with other industries such as IT and utilities, almost all the standard
wireless communication protocols become prominent to the BAS industry.
It is up to the vendor to synergize the protocols with his respective
product mix to obtain an advantage in the market. This article examines the
common wireless protocols and their potential usage in the
BAS market.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth standard is a protocol for exchange of data over short
distance using frequency hopping spread spectrum. It is a packet based
protocol with master slave structure with one master communicating up
to 7 slaves. It has data rate up 3 Mbits/sec. A classic example
for Bluetooth application for BAS industry is during commissioning
stage of Variable Air Volume (VAV) devices. Commissioning of a VAV box
involves entering a calibration factor, minimum and maximum airflows,
size of duct of the box etc… to balance with the airflow of the
building. Typically the values are entered via the BAS vendor’s user
interface. Therefore, backbone BAS network must be operating. However
as we have all seen during commissioning stage the network is not
reliable, other works in the building are performed causing power
outages leading to frustrated commissioning engineers wanting a
reliable network. A great solution to this typical problem is to
implement the Bluetooth protocol at VAV controller, either permanent or
as a plug in device. Also a simple user interface, iPhone or Android
application which then can communicate to the VAV box via
Bluetooth. The commissioning engineer can then communicate to
each VAV box independent of the main BAS network. It permits local
access to each VAV box, allowing an efficient way of commissioning
without the reliance on the BAS network.
ZigBee and its variants
The
ZigBee protocol and its modified variants are becoming the primary
wireless protocol in the BAS industry for communication between
peripheral devices and field controllers. ZigBee is a low cost, low
power wireless mesh network, providing high reliability and extensive
range. Date transmission varies from 20 to 900 KB/Seconds. The protocol
has had significant growth in all markets over the last 5 years, with
the ZigBee Alliance creating specific standard profile for different
markets. ZigBee for Building Automation published recently, developed
in conjunction with BACnet, enables secure and reliable wireless
monitoring of building applications. BACnet has also extended its
protocol to support BACnet over ZigBee to support its current
architecture. Many organizations have taken the ZigBee protocol
and also modified it to come up with their own version of wireless
communication for the building application. The fundamental wireless
architecture is based on the ZigBee platform.
A typical application follows:
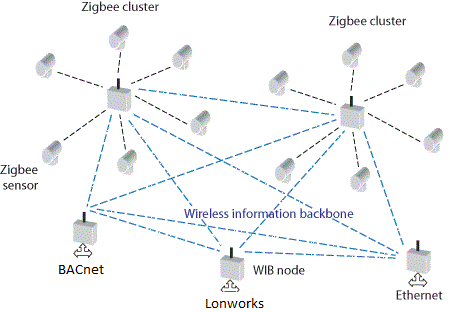
Figure 2: ZigBee Network
As it can seen from figure 2, the temperature sensors dispersed around building communicate back to the router via various repeaters and the built in protocol converter converts the ZigBee data to BACnet where it can be transferred to a field device which controls the AHU that provides the air conditioning for that particular zone.
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
What are the
advantages? The primary advantage is that there is no
requirement to run a cable between the sensor and field device to
connect to a physical input. The non cable run is becoming more
significant in retrofit buildings as access to certain areas is almost
impossible, increasing costs significantly if a cable is required. As
we retrofit older heritage listed buildings, where many access
restrictions are present, wireless sensor peripherals become a great
advantage for the system integrators. I recently observed using ZigBee
based sensors saved drilling a marble wall of a grand ball
room in a large hotel chain.
What diagnosis is available? What happens when battery runs out?
Typically most ZigBee devices contain diagnostic information which is
relayed back to indicated health status. Alarms can be raised to
indicate need to change battery. Some companies have implemented
battery free wireless for maintenance free technology.
The growth of ZigBee protocol will continue to be significant with many
smart grid applications choosing it as the preferred wireless
communication medium for home area networking and management of smart
energy devices. Many electricity hungry home appliances such as washing
machines, dish washers, dryers will have inbuilt ZigBee modules in the
future to communicate back with the grid to participate in demand
response activity to reduce load on the grid and operate at times which
will be beneficial to the consumers.
WiMax
Worldwide interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMax) is a
communication technology for wirelessly delivering high speed data
access for large geographical areas. The fundamental architecture is
similar to Wi-Fi but allows faster data rates and covers larger regions.
It is part of the fourth generation “4G” wireless communication
technology and offers network access to signal radius of up to 50 km
with high data encrypted security.
Figure 3: WiMax Network (Source: howstuffworks)
As seen on the diagram, WiMax connection works as follows:
How
might WiMax communication technology apply to BAS industry? Currently
many vendors are developing many web based user interfaces. However,
the full capabilities of the web technology are not utilized. In theory
once a web server is installed, the system should be able to be
accessed wirelessly anywhere during installation, commission and day to
day running of the system. However, with the typical Wi-Fi connection,
the server cannot penetrate the distance around the entire parameter of
a building from a typical plant room. Also during commissioning where
mobility is highly required, Wi-Fi connection fails at most instances
unless large Wi-Fi infrastructure is setup with repeaters. However,
during initial stages of a building fit out this infrastructure is not
available. Therefore, WiMax technology is an ideal solution for such a
scenario, where the web server is communicating WiMax and smart phones
and PC with WiMax connection can communicate with the server from
anywhere securely at fast data rates. It will be a great benefit
especially at the install and commission stages and also during day to
day management where the building manager can pull up KPI of the
buildings on the go.
The
WiMax technology also can benefit large area BAS setups such as
university campuses, airports and franchises such as hotels located in
multi geographical locations. In campus environments instead of running
cable from building to building or setting up complex Wi-Fi
infrastructures for data sharing between the buildings, a WiMax
solution not only reduces complexity but also has financial savings.
WiMax
is also designed to integrate with existing IP based networks. As most
BAS vendors are developing more and more IP based solutions compared to
low level, low speed protocols and the future integration with the
smart grid, WiMax technology is a great building automation synergy .
As it can be seen, wireless technology can be used in many aspects in
building management systems. It is vital that the industry not only
concentrate on wireless communication for peripheral devices of the
system but also seek carrier grade wireless solutions for faster,
reliable data transfer and integration with other industries. The BAS
industry needs to be proactive with its carrier grade solutions, unlike
its common tendency to be reactive to other industries. A proactive
approach is vital as the smart grid will drive wireless communication
to a new level in the next few years.
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
[Click Banner To Learn More]
[Home Page] [The Automator] [About] [Subscribe ] [Contact Us]